
Understanding Fatigue and Thyroid Disorders
Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by many individuals, and it can be caused by various factors, including lifestyle choices, stress, and medical conditions. One such medical condition that is associated with fatigue is thyroid disorders. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the link between thyroid disorders and fatigue and discuss the importance of seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and management.
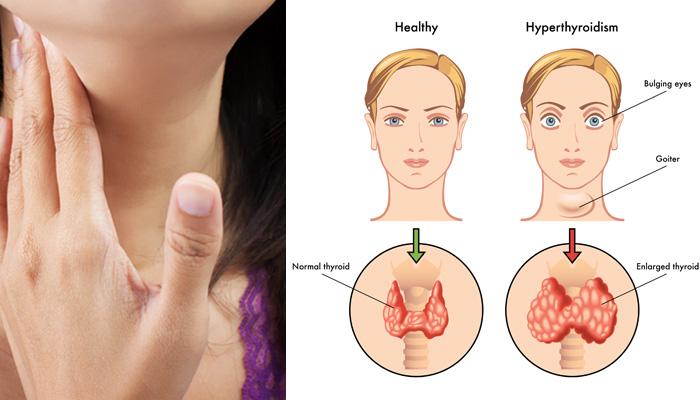
The Thyroid Gland and its Function:
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones that help regulate metabolism and control the body’s energy levels. The two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones influence various organs and tissues, impacting the overall function of the body.
Thyroid Disorders:
Thyroid disorders occur when the thyroid gland produces either too much or too little thyroid hormones. The two most common thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism refers to an underactive thyroid, where the gland does not produce enough hormones, while hyperthyroidism is characterized by an overactive thyroid, leading to excessive hormone production.
The Link between Thyroid Disorders and Fatigue:
Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by individuals with thyroid disorders, particularly in cases of hypothyroidism. When the thyroid gland does not produce sufficient hormones, the body’s metabolism slows down, leading to a decrease in energy levels. This can result in persistent fatigue, weakness, and a feeling of tiredness, even after adequate rest.
Other Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders:
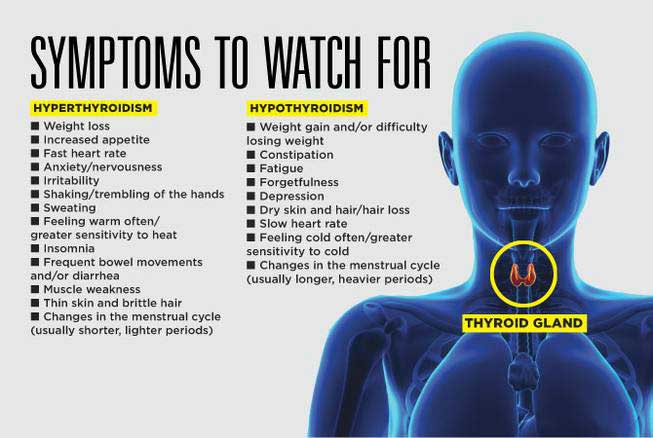
Apart from fatigue, thyroid disorders can cause a range of other symptoms that may vary depending on whether the thyroid is underactive or overactive. Some common symptoms of hypothyroidism include weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, depression, and difficulty concentrating. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism may manifest as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, irritability, anxiety, and tremors.

other relevant factors to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. Once a diagnosis is made, appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
For hypothyroidism, the most common treatment is hormone replacement therapy, where synthetic thyroid hormones are prescribed to compensate for the inadequate hormone production. This can help alleviate fatigue and other associated symptoms. Regular monitoring and adjustments of medication dosage may be necessary to ensure optimal hormone levels.
In the case of hyperthyroidism, treatment options may include medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy to shrink or destroy the overactive thyroid cells, or in some cases, surgery to remove a part or all of the thyroid gland. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of the condition, underlying causes, and individual patient characteristics.
In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can also help manage fatigue associated with thyroid disorders. These include getting adequate rest, practicing stress-reduction techniques, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding substances that may interfere with thyroid function, such as excessive iodine or certain medications.
